The majority of cyber attacks are not occurring due to sophisticated methods by the attackers. They occur due to fundamental weaknesses that are left uncovered by production systems. In thousands of practical security tests and bug bounties, the same groups of vulnerabilities have been re-occurring over and over again. These are simple, disregarded, and easily accessed weaknesses, which are capable of causing some of the most severe breaches.
These vulnerabilities are crucial to the understanding of developers, startups, and even ethical hackers. In the creation of a digital product or in understanding how to be cyber secure, understanding what attackers actually seek is the initial step towards ensuring that systems are well defended.
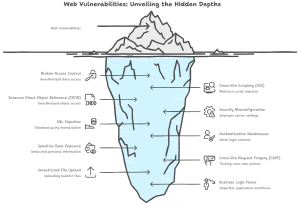
1. Broken Access Control
Broken access control is the situation when users are allowed access to data or do actions, which they are not supposed to do. This can make attackers easily look at, alter, or delete the information of other users by merely altering identifiers in requests. It is also one of the most prevalent and serious faults in practical uses since they can cause the direct leakage of data and account takeovers.
2. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
The Cross-site Scripting means that an attacker can inject malicious scripts into the web pages being accessed by other individuals. XSS can be used to steal session cookies, steal accounts and alter the content of websites when exploited. It is usually committed where the applications receive user input and present it without the necessary checking or coding. Even after being famous, XSS still seems to be a common occurrence in contemporary web applications.
3. Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR)
The IDOR vulnerabilities happen when the application provides internal object names, like user names, order numbers, or file names, and does not authenticate the access permissions. Hackers will just have to alter such values to obtain unauthorized access to the data of other users. IDOR is very prevalent in APIs and poorly written backend systems.
4. Security Misconfiguration
Security misconfiguration is described as the improperly configured servers, databases, cloud storage or application settings, which reveal sensitive information or administrative interfaces. This involves open administration panels, open debug endpoints, default passwords and public backups. These problems are readily vulnerable and frequently lead to complete system breach.
5. SQL Injection
With SQL Injection, attackers can control the query in databases by using susceptible input forms. Attackers are able to retrieve, alter, or destroy vulnerable data and in some cases, they are able to have complete access to the database server when they are successful. SQL Injection is one of the most effective attacks that vulnerable legacy systems may be exposed to despite the fact that the modern frameworks minimize its existence.
6. Authentication and Session Management Weaknesses
The use of weak authentication controls enables an attacker to avoid logging in, reuse a token or engage in brute force. Such weaknesses usually lead to the seizure of accounts and/or access to guarded systems unlawfully. Typical causes include poor session expiration, predictable tokens, and the lack of rate limits.
7. Sensitive Data Exposure
Sensitive data exposure is a situation where the apps do not secure the personal information, passwords, payment details, or internal system data. This is usually due to the absence of encryption or poor cryptography or inappropriate data storage. Bare sensitive information can be utilized to commit identity theft, fraud, and other attacks.
8. Cross-site Request Forgery (CSRF)
CSRF tricks users into executing some actions that they do not want to execute, including changing passwords or transferring money. This is a weakness that arises when the applications fail to verify the origin of requests. It is particularly harmful in authenticated surroundings.
9. Unrestricted File Upload
Free file uploading vulnerabilities enable attackers to post harmful files on the servers and execute them in order to take over the system. This may cause complete compromise of the server and loss of data. The most common causes are poor validation of file types and storage locations.
10. Business Logic Flaws
Business logic flaws are those applications that act in manners other than what the developers intended. Such vulnerabilities are not introduced by technical errors but rather by imperfect workflows that are accessible to attackers and allow them to take advantage of it either financially or functionally. These are some of the most difficult vulnerabilities to be identified as well as lead to significant financial losses.
Final Thoughts
Most of the real-life violations are not based on sophisticated hacking. They are occurring since fundamental vulnerabilities are not taken into account in the process of development and deployment. These are some of the most prevalent pitfalls that can be learned to create secure systems and be a good ethical hacker.
You can be a developer attempting to secure your product, or you can be a learner attempting to join the field of cybersecurity, but it will be the real experience more than the theory. Bugv offers a trusted platform in Nepal on which ethical hackers can find real vulnerabilities and companies defense of what really matters.
Start your journey with real-world security testing today at Bugv.